File类
File是Java中的文件类,用于处理和文件相关的一些操作,例如文件的创建,删除等等。
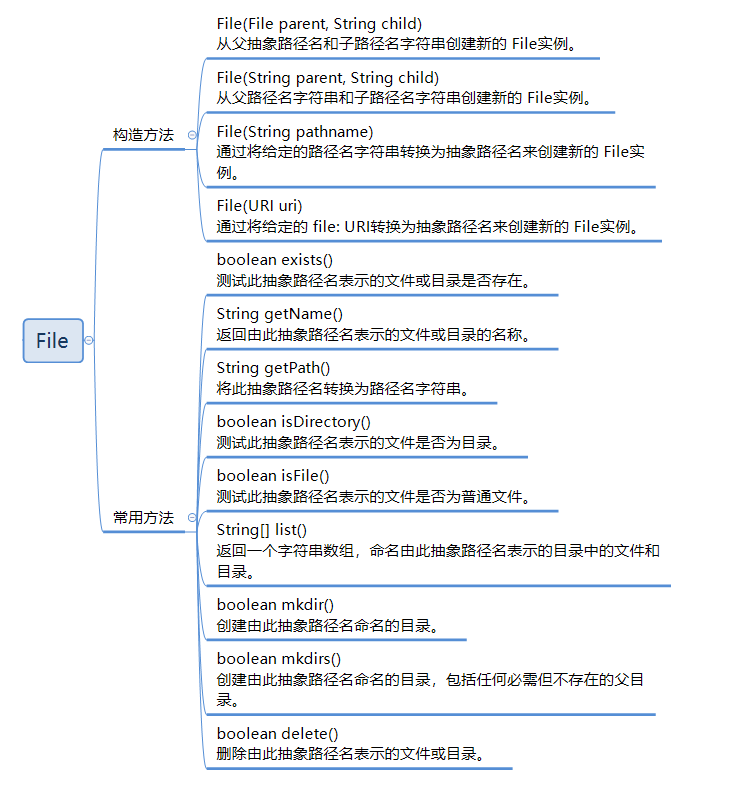
构造方法
- File(File parent, String child)
从父抽象路径名和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。
- File(String parent, String child)
从父路径名字符串和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。
- File(String pathname)
通过将给定的路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建新的 File实例。
- File(URI uri)
通过将给定的 file: URI转换为抽象路径名来创建新的 File实例。
常用方法
- boolean mkdir()
创建由此抽象路径名命名的目录。
- boolean mkdirs()
创建由此抽象路径名命名的目录,包括任何必需但不存在的父目录。
- boolean delete()
删除由此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录。
- boolean exists()
测试此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录是否存在。
- String getName()
返回由此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录的名称。
- String getPath()
将此抽象路径名转换为路径名字符串。
- boolean isDirectory()
测试此抽象路径名表示的文件是否为目录。
- boolean isFile()
测试此抽象路径名表示的文件是否为普通文件。
- String[] list()
返回一个字符串数组,命名由此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件和目录。
IO流
所谓IO流,便是Input和Output,即输入流和输出流,具体是指文件的输入流和输出流。
IO流分为很多类,其中最为常用的就是IO字节流和IO字符流,除此之外,还有缓冲流,转换流,序列化流,打印流等等。
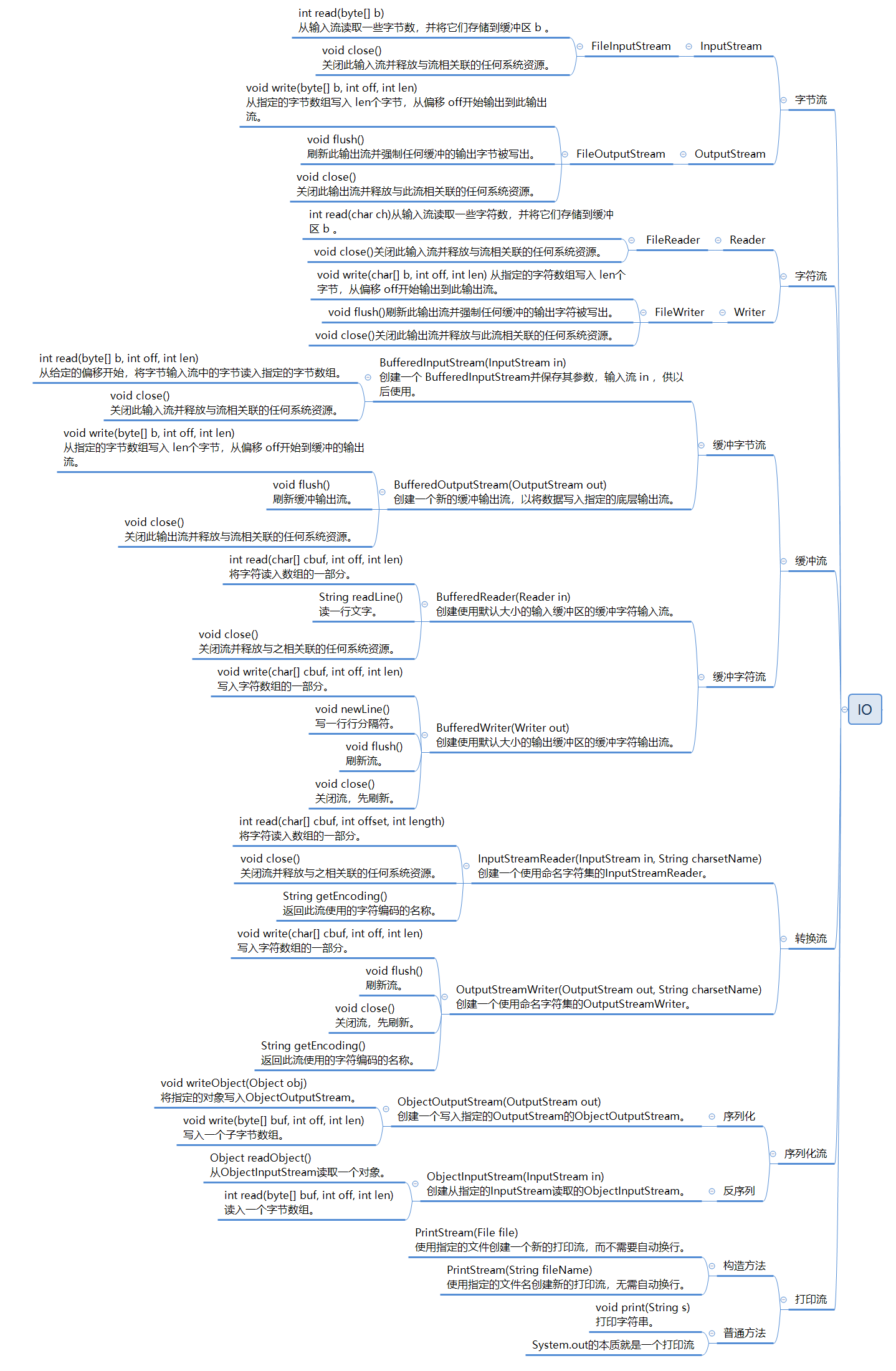
IO字节流
IO字节流有两个上层接口,分别是InputStream和OutputStream接口,我们常用的具体实现类有FileInputStream和FileOutputStream,即文件输入字节流和文件输出字节流。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| int read(byte[] b) |
从输入流读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到缓冲区 b 。 |
| void close() |
关闭此输入流并释放与流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) |
从指定的字节数组写入 len个字节,从偏移 off开始输出到此输出流。 |
| void flush() |
刷新此输出流并强制任何缓冲的输出字节被写出。 |
| void close() |
关闭此输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
IO字节流代码示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("b.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fos.flush();
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
|
IO字符流
IO字符流有两个上层接口,分别是Reader和Writer接口,我们常用的具体实现类有FileReader和FileWriter,即文件输入字符流和文件输出字符流。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| int read(char ch) |
从输入流读取一些字符数,并将它们存储到缓冲区 b 。 |
| void close() |
关闭此输入流并释放与流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| void write(char[] b, int off, int len) |
从指定的字符数组写入 len个字节,从偏移 off开始输出到此输出流。 |
| void flush() |
刷新此输出流并强制任何缓冲的输出字符被写出。 |
| void close() |
关闭此输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
IO字符流代码示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.txt");
char[] ch = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fr.read(ch)) != -1) {
fw.write(ch,0,len);
}
fw.flush();
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
|
缓冲流
缓冲字节流
- BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
创建一个 BufferedInputStream并保存其参数,输入流 in ,供以后使用。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) |
从给定的偏移开始,将字节输入流中的字节读入指定的字节数组。 |
| void close() |
关闭此输入流并释放与流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
- BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将数据写入指定的底层输出流。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) |
从指定的字节数组写入 len个字节,从偏移 off开始到缓冲的输出流。 |
| void flush() |
刷新缓冲输出流。 |
| void close() |
关闭此输出流并释放与流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
缓冲字节流代码示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("b.txt"));
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bos.flush();
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
|
缓冲字符流
- BufferedReader(Reader in)
创建使用默认大小的输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) |
将字符读入数组的一部分。 |
| String readLine() |
读一行文字。 |
| void close() |
关闭流并释放与之相关联的任何系统资源。 |
- BufferedWriter(Writer out)
创建使用默认大小的输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) |
写入字符数组的一部分。 |
| void newLine() |
写一行行分隔符。 |
| void flush() |
刷新流。 |
| void close() |
关闭流,先刷新。 |
缓冲字符流代码示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("b.txt"));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
|
转换流
- InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName)
创建一个使用命名字符集的InputStreamReader。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| int read(char[] cbuf, int offset, int length) |
将字符读入数组的一部分。 |
| void close() |
关闭流并释放与之相关联的任何系统资源。 |
| String getEncoding() |
返回此流使用的字符编码的名称。 |
- OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName)
创建一个使用命名字符集的OutputStreamWriter。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) |
写入字符数组的一部分。 |
| void flush() |
刷新流。 |
| void close() |
关闭流,先刷新。 |
| String getEncoding() |
返回此流使用的字符编码的名称。 |
转换流代码示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("a.txt"),"UTF-8");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("b.txt"),"UTF-8");
char[] ch = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = isr.read(ch)) != -1) {
osw.write(ch,0,len);
}
osw.close();
isr.close();
}
|
序列化流
- ObjectInputStream(InputStream in)
反序列化流:创建从指定的InputStream读取的ObjectInputStream。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| Object readObject() |
从ObjectInputStream读取一个对象。 |
| int read(byte[] buf, int off, int len) |
读入一个字节数组。 |
- ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out)
序列化流:创建一个写入指定的OutputStream的ObjectOutputStream。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| void writeObject(Object obj) |
将指定的对象写入ObjectOutputStream。 |
| void write(byte[] buf, int off, int len) |
写入一个子字节数组。 |
【注意】需要序列化的对象,必须要实现Serializable接口。
序列化流代码示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"));
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));
oos.writeObject(new User(1,"张三","123"));
User user = (User) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(user);
oos.close();
ois.close();
}
|
打印流
- PrintStream(File file)
使用指定的文件创建一个新的打印流,而不需要自动换行。
- PrintStream(String fileName)
使用指定的文件名创建新的打印流,无需自动换行。
| 常用方法 |
描述 |
| void print(String s) |
打印字符串。 |
System.out的本质就是一个打印流
打印流代码示例:
1
2
3
4
| public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(new File("a.txt"));
out.print("打印流");
}
|
思维导图